|
| |
Metallothionein- The Stress Protein
Homeopathic remedies will help a person with metallothionein and other
nutritional deficiencies. Contact us to learn more.
Click Here to Buy Remedies and Supplements from Homeopathic Remedies Online Store
What Is
Metallothionein?
-
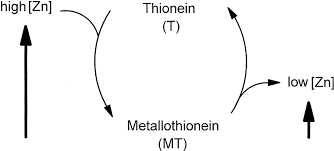
Metallothionein
is
an essential protein that carries out very vital functions in the body.
-
One of its most important
functions is the protection against heavy metals.
-
High
concentrations of this protein are present in the mucous membrane of the
intestine
-
Metallothionein
serves as a binding agent for heavy metals by exchanging
zinc for mercury, lead, platinum, aluminum, etc.
-
Metallothionein
is
found in the
liver, pancreas, mouth, stomach and brain.
-
It is made up
of 60 to 70 amino acids and 7 atoms of zinc.
-
A deficiency of this essential protein may lead to all kinds of problems in
the development of the child.
-
Children
with a dormant metallothionein deficiency
run the increased risk of developing symptoms caused by all kinds of
environmental factors.
-
The symptoms include autism spectrum,
ADHD and other behavioral disorders,
cancer, chronic fatigue syndrome,
fibromyalgia, and others.
-
It is significant to note that those with
various cancers show high copper and low
zinc
levels in lab testing.
-
Cadmium replaces
zinc in
metallothionein and is so strongly attracted that it is very difficult to
remove.
-
Metallothionein function in the bowels and the brain can be
restored with the use of zinc.
-
Increasing metallothionein functions is done using an
ascorbate complex (water soluble vitamin C) combined
with potassium, magnesium and zinc. This combination also restores the
integrity of the bowels
-
In addition, the use of the homeopathic remedy Saccharum
Officinale 6C (potentized sugar) gives good results in restoring intestinal
flora and function.
From the CEASE website:
https://www.cease-therapy.com/treatment/metallothionein/
"Metallothionein is
involved in many functions of the body, including immunity, brain and
gastrointestinal tract maturation, and the regulation of metals.
Metallothionein is essential for maintenance of the proper ratio of
copper to zinc. So much so, that a zinc/copper imbalance is the main
indicator for a metallothionein malfunction. The malfunction could be
due to a genetic weakness but may also be primarily induced by
nutritional deficiencies and imbalances. The primary nutrient needed in the
formation of metallothionein is zinc.
Therefore, metals that
compete with zinc such as mercury and cadmium will eventually disturb
metallothionein function. Metallothionein is crucial to the body in
regulating and coping with toxic metals. It envelopes metals such as
mercury, lead and cadmium, binding with them and carrying them out of the
body. Mercury or lead in the gut require metallothionein in order to
disable the toxic substance.
When mercury is ingested
in any form, it produces destructive changes in the mucous membrane linings
of the gastro-intestinal tract. It enters the blood circulation, travels to
the tissues, and then damages literally every cell with which it comes into
contact. Mercury has a long history of use as a disinfectant and
antibiotic. It is still used as an antibacterial preservative
so it is certain that it would kill at least some of the flora. Ideally,
ingested mercury is bound to metallothionein and transported out of the body
through the bile and through the kidneys.
Without the effect of
metallothionein, the toxic metals will interact with chemicals called
sulfhydral groups. A combination of sulphur and hydrogen, these groups
have tremendous power to bind to mercury, lead, and cadmium but especially
mercury. Among the sulfhydral groups in the intestines are the enzymes
that break down casein and gluten.
Toxic metals and
low zinc interfere with the enzyme functions giving rise to gluten
intolerance to grains such as wheat, rye, barley and oats and to dairy
intolerance."
Metallothonein
Plays A Key Role in Processes in the
Body
-
Metallothonein regulates
zinc and
copper and zinc
concentrations in the blood.
-
Essential in the development and functioning of our immune system.
-
Key nutrient
in the development of nerve cells in the brain along with the
Omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Protects
against excessive yeast overgrowth in the intestines.
-
Prevents
intestinal infections.
-
Involved in gastric acid production.
-
Influences
taste and texture sensation of food in the mouth.
-
Regulates hippocampal
behavior.
-
Involved in the emotional development and socialization (amygdala).
| |
|